
views
Introducing Budget Management

Explain how to accurately estimate income and expenses. Make a spreadsheet or write a sample monthly budget with a pen and paper. List total income, and break expenses up into categories, such as car payments, insurance, a cell phone bill, and entertainment. Mention that income and expenses can fluctuate month to month, so tracking them over time is important.

Make the sample budget relevant for your student or child. For instance, include your teenager’s actual income and spending from last month. List after-tax income from their part-time job and add up their car insurance, cell phone bill, clothes, haircut, and money spent going out with friends. Start with these basic examples, then introduce a more complex sample budget that includes rent, utilities, and groceries. For younger students, use simple values, such as a $10 weekly allowance and candy, toys, and other small expenses.
Explain the difference between a need and a want. Tell your learner that housing, utilities, and other core bills are spending priorities. If money’s tight, paying rent or car insurance is more important than going out to eat or buying a new cell phone. Subtract their expenses from income, and discuss how balancing needs and wants impacts their budget. Ask them to identify needs that take priority and wants that can be cut to save money.

Show them how to make bill payments. Mention that the most common ways to pay bills are via check or debit. Show them a physical check and explain how to fill in the date, payee, payment amount, and signature fields. Then go to an online bill payment portal and explain how to fill in debit card billing information.

Introduce the importance of saving money. While saving money is a distinct topic with its own lesson plan, you’ll need to mention it when you explain budgeting. Let them know that saving 10 to 20 percent of their income is crucial, and they’ll need to save more of their income as they get older. Include specific reasons to save, such as for an emergency, a down payment on a home, and retirement. You can also teach them to create different savings to help them save for multiple goals. Show them that they can even physically put money into separate jars or envelopes to keep track of how much they've saved. EXPERT TIP Paridhi Jain Paridhi Jain Certified Public Accountant Paridhi Jain is a Certified Public Accountant and the Co-Founder of Seva Ltd, a CPA firm operating in Maryland and Alabama. She has over 10 years of professional experience in the financial sector and has built a reputation for assisting small business owners navigate the intricacies of regulatory compliance, encompassing areas from company structuring and entity formation to detailed nexus determinations for income and sales tax. She is an active member of the Alabama Society of CPAs and has a certification in pre-professional accounting. She graduated Magna Cum Laude from the University of Maryland, Baltimore County with a major in Information Systems. Paridhi Jain Paridhi Jain Certified Public Accountant Early financial literacy empowers children to make smart money choices later as adults. Teach children about money early. Kids can start grasping basic ideas like exchange rates, savings interest, and how money relates back to work effort. Building this foundation through life lessons will set up positive money habits that last a lifetime.

Use budgeting resources to simulate real-world scenarios. After covering the basics, have your learner create and manage hypothetical budgets using smartphone apps. Personal finance simulators can provide accessible, concrete examples and reinforce budget management skills. For example, use the Budget Challenge app, which is free for iOS and Android devices: https://www.budgetchallenge.com.
Explaining Credit and Debt

Define credit and its broad impacts on life. Explain that credit is when a lender gives you money and expects you to pay it back by a due date or with interest, which is an added percentage. Tell them that if they don’t repay a line of credit, they’ll have a harder time getting leases, mortgages, cars, jobs, and other life essentials. Understanding credit is an important first step towards financial literacy. If the person already has some debt, you can also help them come up with a basic payment plan for handling that debt.
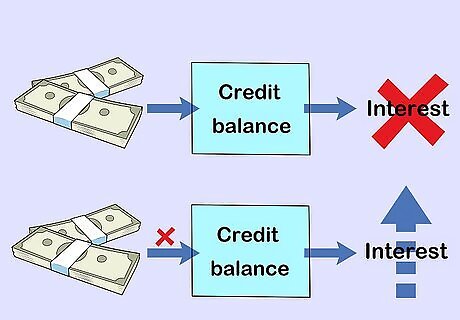
Describe how interest works. Explain that they won’t have to pay interest if they pay off a credit card balance by its due date. Mention that the better credit you have, the lower your interest rate will be on credit cards, mortgages, and car loans. Explain that interest on a loan can capitalize if it’s not paid, which is when it becomes part of the principle, or original loan amount. Compare a credit balance with library books to help them understand. If they return the book they borrowed, they won’t have to pay extra. If they keep the book past its due date, they’ll have to pay extra, or interest.
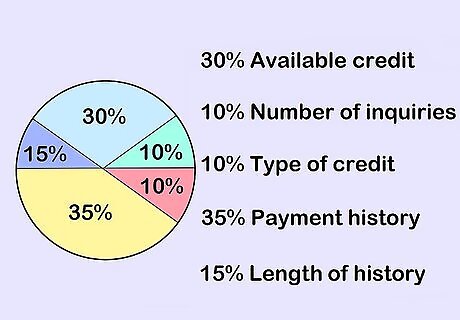
Explain how credit scores are calculated. Tell your student that it takes time to earn a good credit score. Explain that the score is based on payment history, amounts owed, length of credit history, new credit and recently opened accounts, and types of credit in use. Stress that a low number will negatively impact their ability to get loans, leases, jobs, and other necessities.

Stress the importance of using a credit card responsibly. Let them know that having a credit card is an important part of building credit, but they must use it responsibly. Tell them they can’t use the card to make a purchase they can’t afford. Remind them of the library book analogy to stress the importance of paying of a balance by the due date. Mention that if they don’t pay off a balance and credit card debt piles up, their credit score will take a major hit.
Spelling out Savings and Investments
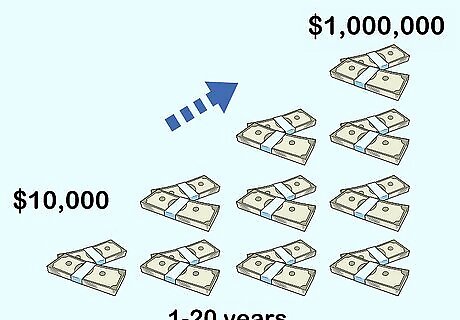
Discuss the importance of saving and growing money. Remind them of the reasons that they need to save, from emergencies to retirement. Explain that money can grow when invested properly. Mention that, while there are risks, if they invest $10,000, they can earn tens of thousands of dollars over the course of 20 years.
Describe how checking and savings accounts work. Explain that a checking account is primarily used for making payments and a savings account is for holding money. Mention that bank accounts earn interest, and a savings account earns more interest and should be left alone. Teach them to automatically put away a little money each time they receive any. For instance, if they're working, they might put $25 out of each paycheck into a savings account.
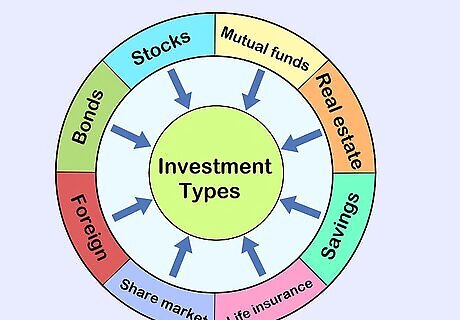
Explain the various types of investments. Tell your learner that, as they get older, they should think about investing money in the stock market. Let them know that there are risks, but investments are a good way to grow money for retirement. Explain that there are a variety of ways to invest money, and go over the basic types of investments. Stocks are when you purchase a small amount of ownership in a company. If the company performs well, your investment becomes more valuable. Mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are pools of money from lots of investors that are used to purchase a diverse range of investments. Since they hold dozens or hundreds of securities, or investments, they’re less risky than purchasing stock in a single company. Bonds are when you lend money to a government or a business for a specific length of time at a fixed interest rate. While they’re lower risk, bond earnings are lower-yield investments.
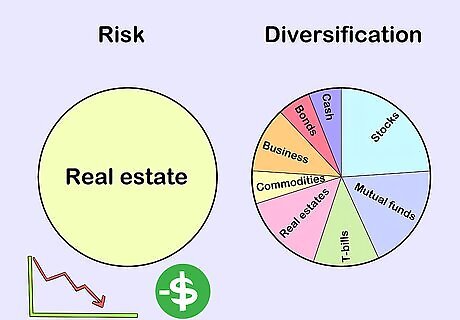
Discuss risk and diversification. After introducing basic types of investments, tell your learner that each has a degree of risk. If they invest in 1 company that goes under, their investment will lose value. In order to lower their risk, they need to diversify, or invest in many companies and other investment categories (such as natural resources or real estate).
Use stock market games to simulate investing. After introducing the basics, have your student play investment simulation games. Smartphone apps can help make complex, abstract aspects of investing more concrete and accessible. Wall Street Survivor is a helpful free resource: http://www.wallstreetsurvivor.com.


















Comments
0 comment