
views
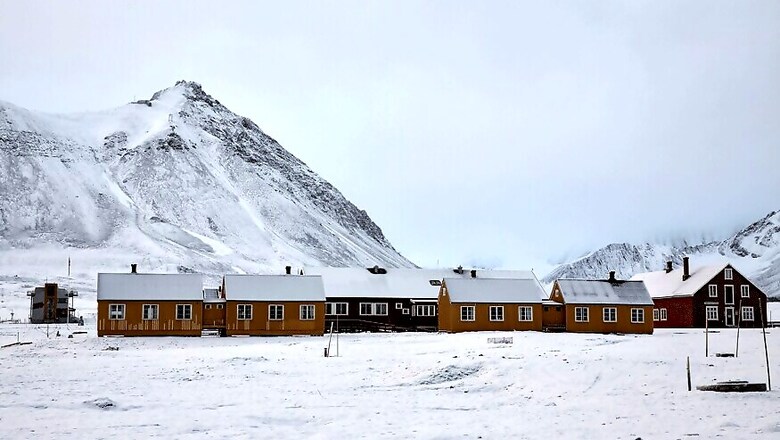
Stockholm: The Arctic archipelago of Svalbard has seen such extreme warmth this year that the average annual temperature could end up above freezing for the first time on record, scientists said on Friday.
Ketil Isaksen of the Norwegian Meterological Institute said that the average temperature in Longyearbyen, the main settlement in Svalbard, is expected to be around 0 Celsius (32 Fahrenheit) with a little over a month left of the year.
"This is a little bit shocking," Isaksen said. "If you had asked me five or 10 years ago, I could not have imagined such numbers in 2016."
The normal yearly average in Svalbard, an island group midway between the North Pole and continental Norway, is minus 6.7 C (20 F) and the warmest year until now was 2006, when the average temperature in Svalbard was minus 1.8 C (29 F), Isaksen said.
"Svalbard is a very good spot to show what's happening in the Arctic at the moment," he said, noting that each of the past 73 months has been warmer than average.
The rising temperatures in the Arctic are affecting permafrost and snow cover as well as the amount of sea ice, which this year was the second-lowest on record. Isaksen said the sea ice is building up much slower than normal as winter approaches.
"There are still huge areas in the Barents Sea and Kara Sea to the east of Svalbard that are free of ice," he said. "They should normally be ice-covered."
Scientists believe the loss of sea ice accelerates the warming because ice reflects sunlight back into space while the darker surface of the ocean absorbs most of the radiation.
A report released Friday by the Stockholm Environment Institute identified the decline in sea ice cover and the thinning of the Greenland ice sheet among several "regime shifts" happening in the Arctic as a result of climate change.
"These regime shifts affect the stability of the climate and landscape, plant and animal species' ability to survive, and indigenous peoples' subsistence and ways of life," the institute said.
Several studies show the world as a whole is on track for a new heat record this year, with the El Nino weather phenomenon adding to the underlying warming trend.



















Comments
0 comment