
views
Understanding Arbitrage and The Forex Market

Understand the foreign exchange market. The foreign exchange market, commonly referred to as forex, is an international exchange for the trading of currencies. It allows investors (from large banks to individuals and everyone in between) to trade one national currency for another. Each trade is both a purchase and a sale, as one currency is sold in order to buy another one. This duality means that each currency is priced only in relation to another currency. In other words, a U.S. dollar has a price only in terms of British pounds, Japanese yen, Mexican pesos, or some other national currency. The forex market also facilitates the sale of financial instruments, including forwards, swaps, options, and others. These are more complicated than simple currency trades and can involve a multitude of other trading tactics.

Learn about arbitrage. Arbitrage is the practice of buying an asset in one market and immediately selling it at a slightly better price elsewhere. In theory, a given currency should carry the same price in different markets. However, market inefficiencies (often resulting from communication difficulties) may result in different prices emerging in different locations at the same time. Arbitrage takes advantage of these inefficiencies to the benefit of the trader. For example, if a trader recognizes that a currency can be bought for less in one market and sold for more in another, he could then make those trades and keep the difference between the purchase and the sale.
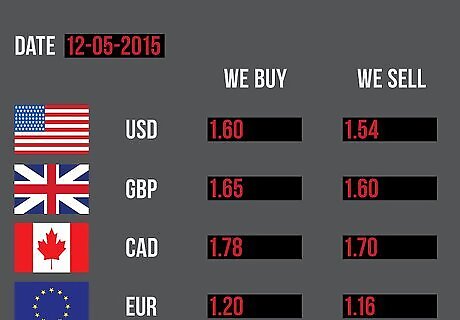
Know how to use arbitrage to make profitable trades. Forex traders take advantage of minor price differences by buying currencies where they are less valuable and selling them where they are more valuable. This usually involves multiple trades of intermediate currencies in practice. Intermediate currencies are other currencies used to express the value of the currency you are trading. You wouldn't just buy and sell U.S. dollars, for example. You might buy euros with your dollars and sell them for pounds, with which you could then buy dollars. For a more specific example, imagine that you could use 2 American dollars ($) to buy 1 British pound sterling (£), then use that pound to buy 1.50 euros (€), and then use the l.50 euros to buy $2.50. By trading this way you have gained $0.50, simply by exploiting price differences. In the real world, price differences would never be this extreme. In fact, they are usually fractions of a cent. Traders make money by trading in large volume. Volume trading allows traders to make enough profit to offset transaction fees. In addition, traders must overcome the fact that arbitrage opportunities may disappear only a few seconds after first appearing (as markets adjust to correct the difference in pricing). Institutional traders rely on computers and automated trading to buy and sell currencies quickly enough to stay ahead of the markets.
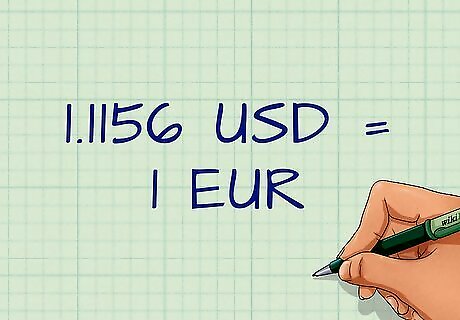
Know how to read currency prices. Market prices are expressed in a very specific way. As mentioned, currencies are priced in relation to other currencies. The US dollar (USD) is often used as a base currency in determining values. For example, the value of the Japanese yen (JPY) will be expressed as a ratio of dollars to yen (USD/JPY). The relative values of currencies are generally expressed to four decimal places. For example, the euro-to-dollar rate might be expressed as 1.1156 EUR/USD. This means that at a given moment it would take 1.1156 US dollars to buy one euro.
Calculating Arbitrage
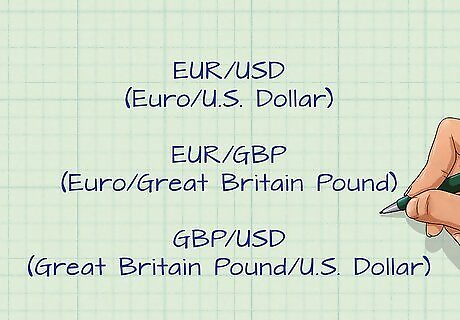
Determine what currencies to use. In order to have a triangular arbitrage, you must compare the exchange rate of three "currency pairs" that you can trade between. An example of this is the EUR/USD (euro/dollar), EUR/GBP, (euro/Great Britain pound) and GBP/USD (pound/dollar). As in any such triangular arrangement, there are three currencies involved, and each currency is paired separately with each of the other two.

Get the current exchange rate for each pair. You can find the current exchange rate in your forex broker's software (if you have a forex broker) or on websites that have the current exchange rates listed. For illustration, assume the following exchange rates for the euro (EUR/€), the British pound (GBP/£), and the U.S. dollar (USD/$). Exchange rate of EUR/USD is 1.2238, which means that you will have to spend about $1.22 to buy €1. Exchange rate for GBP/EUR is 1.1910, which means that you can buy £1 for about €1.19 Exchange rate for GBP/USD is 1.4650, which means that for £1, you can buy about $1.47.
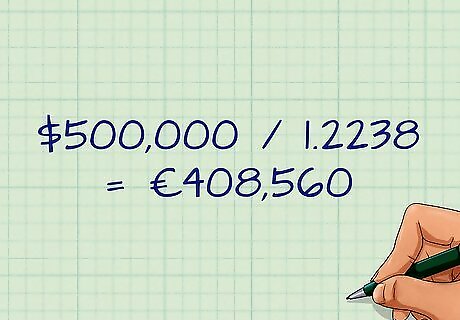
Calculate the arbitrage. The arbitrage is made by buying and selling the correlating currencies against each other. Currency is traded in what are called "lots." Standard lots are blocks of 100,000 units of a currency, and mini-lots are blocks of 10,000 units. Imagine you have the ability to make a leveraged trade with $500,000. A leveraged trade is one made mostly with debt. Spend your $500,000 to buy euros. Because the USD is on the bottom of the exchange quote (EUR/USD), divide the $500,000 by the quoted amount. So $500,000/1.2238 would net you about €408,560. Sell the euros for British pounds. Because the euro is on the bottom of this exchange rate (GBP/EUR), we divide the number of euros by the exchange rate to get the number of pounds. So, dividing €408,560 by 1.1910, we get about £343,040. Sell the British pounds for U.S. dollars. Here, the GBP is on top of the quote (GBP/USD), so we multiply the number of pounds by the exchange rate to get the number of USD. So, £343,040 multiplied by 1.4650 yields roughly $502,550. Determine your profit. You started with $500,000, and you now have $502,550 after a few simple trades. Your profit is $502,550 - $500,000, or $2,550.
Using Arbitrage as a Trading Strategy

Get access to a forex trading platform and software. Brokers and traders who trade arbitrage don't calculate arbitrage manually. They use software programs that can identify opportunities in the market and calculate the arbitrage in seconds. The software can be set up to buy and sell at the precise moment that the opportunity arises. You can access similar platforms online and trade in the forex market. Search for "online forex trading" to see what types of software are currently available. Be aware that many of these platforms charge a trading fee. Such a fee will diminish (or even erase) your profit on each trade, particularly if you're trading with limited capital.
Beware of faulty arbitrage programs. There are forex arbitrage software programs for sale online. Before using these programs on a real account, try them on a demonstration account first. This will prevent the loss of money through the use of faulty software. Have an experienced arbitrageur recommend software and trading platforms.
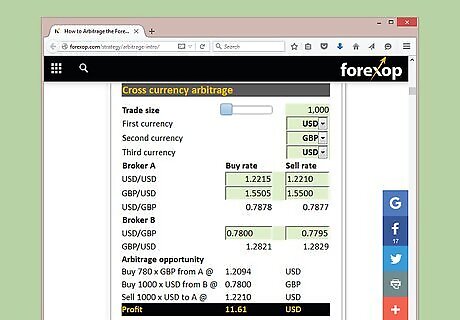
Look for arbitrage opportunities. Some online forex trading platforms offer calculators or automated programs for finding arbitrage opportunities. Take advantage of this service if your trading platform offers it. You can also use an independent forex arbitrage calculator to determine if an arbitrage opportunity exists. These are available online, sometimes free and sometimes for a fee. Try searching for "arbitrage calculator" to find one.
Don't hesitate. It doesn't take long for markets to correct themselves when an arbitrage opportunity presents itself. You'll have to act quickly to make a trade before the chance is lost. Once you see a price difference, grab it immediately. The reality is that with the current level of technology and ease of worldwide communication, forex arbitrage is typically profitable only for large financial institutions with lightning-fast trading systems. This is because arbitrage opportunities usually evaporate in a matter of seconds.



















Comments
0 comment