
views
Calculating the List Price

Assess what information you know. In order to calculate the list price, or the original price, of an item on sale, you need to know what the sale price is, and what the discount percent is. For example, you might know that a sweater is on sale for $51.75 after a 25% discount.

Convert the discount percent to a decimal. Remember that percents are hundredths, so to convert, either divide the percent by 100, or simply place a decimal after the number and move it two places to the left. For example, 25% expressed as a decimal is .25.

Set up an equation for finding the original price of a discounted item. Use the formula S = P − P D {\displaystyle S=P-PD} S=P-PD, where S {\displaystyle S} S equals the sale price of the item, P {\displaystyle P} P equals the original price of the item, and D {\displaystyle D} D equals the discount percent of the item.

Plug the sale price into the formula. Make sure you substitute for the variable S {\displaystyle S} S. For example, if the sales price is $51.75, your formula will look like this: 51.75 = P − P D {\displaystyle 51.75=P-PD} 51.75=P-PD.
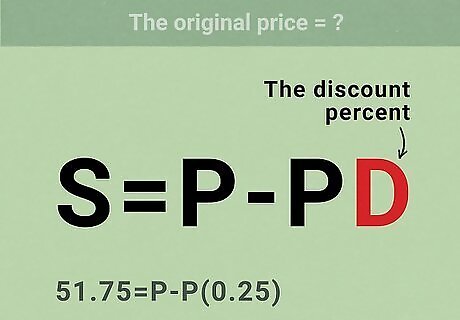
Plug the discount percent into the formula. Make sure you use the decimal form of the discount, and substitute for the variable D {\displaystyle D} D. For example, if the item is 25% off, your formula will look like this: 51.75 = P − P ( .25 ) {\displaystyle 51.75=P-P(.25)} 51.75=P-P(.25).

Use the distributive property to simplify the formula. To do this, pull out the variable P {\displaystyle P} P. For example: 51.75 = P − P ( .25 ) {\displaystyle 51.75=P-P(.25)} 51.75=P-P(.25) 51.75 = P ( 1 − .25 ) {\displaystyle 51.75=P(1-.25)} 51.75=P(1-.25)

Complete the calculation in parentheses. This will give you the percent of the item’s original price that the sales price represents. For example, 1 − .25 = .75 {\displaystyle 1-.25=.75} 1-.25=.75. So, if an item is 25% off, you would only pay 75% of the original price to purchase the item on sale. Your formula will look like this: 51.75 = P ( .75 ) {\displaystyle 51.75=P(.75)} 51.75=P(.75).

Divide each side of the equation by the percent of the original price. This will give you the value of P {\displaystyle P} P, the list price of the item. For example: 51.75 = P ( .75 ) {\displaystyle 51.75=P(.75)} 51.75=P(.75) 51.75 .75 = P ( .75 ) .75 {\displaystyle {\frac {51.75}{.75}}={\frac {P(.75)}{.75}}} {\frac {51.75}{.75}}={\frac {P(.75)}{.75}} 69 = P {\displaystyle 69=P} 69=PSo the original price of a sweater marked $51.75 after a 25% discount is $69.00.
Calculating the Sale Price

Assess what information you know. In order to calculate the sale price of an item, you need to know what the original or list price is, and what the discount percent is. For example, you might know that a sweater is $69 and on sale for 25% off.

Convert the discount percent to a decimal. Remember that percents are hundredths, so to convert, either divide the percent by 100, or simply place a decimal after the number and move it two places to the left. For example, 25% expressed as a decimal is .25.

Multiply the original price by the discount percent. Make sure you use the decimal form of the percent. This will give you the discount, in dollars, off the original price. For example, 69 × .25 = 17.25 {\displaystyle 69\times .25=17.25} 69\times .25=17.25. So, $17.25 is the discount off the original price.

Subtract the discount amount from the original price of the item. This will give you the sale price. For example, 69 − 17.25 = 51.75 {\displaystyle 69-17.25=51.75} 69-17.25=51.75. So, the sale price of a $69 sweater that is 25% off is $51.75.
Calculating the Discount

Assess what information you know. In order to calculate the discount percent of an item, you need to know what the sale price is, and what the original or list price is. For example, you might know that a sweater’s original price is $69, and that it is on sale for $51.75.

Subtract the sale price from the original price. This will give you the markdown amount, the amount of dollars taken off the original price. For example, since 69 − 51.75 = 17.25 {\displaystyle 69-51.75=17.25} 69-51.75=17.25, $17.25 was taken off the price of the sweater.

Set up a discount formula for your item. Use the formula M = P D {\displaystyle M=PD} M=PD, where M {\displaystyle M} M equals the markdown, in dollars, of the item, P {\displaystyle P} P equals the original price of the item, and D {\displaystyle D} D equals the discount percent of the item.

Plug the original price and the markdown into the formula. Be sure to substitute the original price for the variable P {\displaystyle P} P, and the markdown for the variable M {\displaystyle M} M. For example, if a sweater, originally $69, has a markdown of $17.25, your formula will look like this: 17.25 = 69 D {\displaystyle 17.25=69D} 17.25=69D.

Divide each side of the equation by the original price. This will give you the percent of the discount as a decimal. To convert to a percent, move the decimal point two places to the right. For example: 17.25 = 69 D {\displaystyle 17.25=69D} 17.25=69D 17.25 69 = 69 D 69 {\displaystyle {\frac {17.25}{69}}={\frac {69D}{69}}} {\frac {17.25}{69}}={\frac {69D}{69}} .25 = D {\displaystyle .25=D} .25=DSo, a $69 sweater on sale for $51.75 is 25% off.



















Comments
0 comment