views
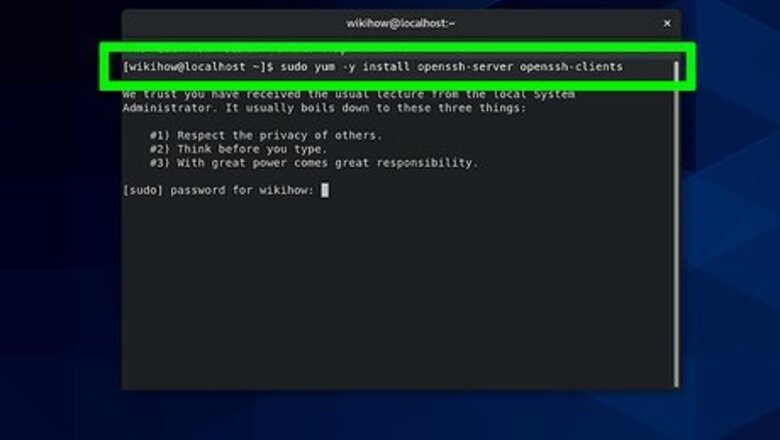
- Enter this code into your command-line utility:
sudo yum -y install openssh-server openssh-clientssudo systemctl start sshd-
sudo systemctl status sshd. - You should now see an "active" status.
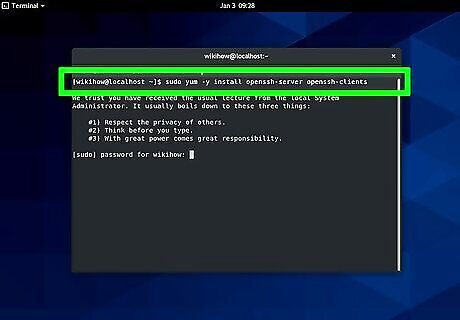
Enter the following code into your command-line utility: sudo yum -y install openssh-server openssh-clients. This code installs the appropriate SSH server and client type.
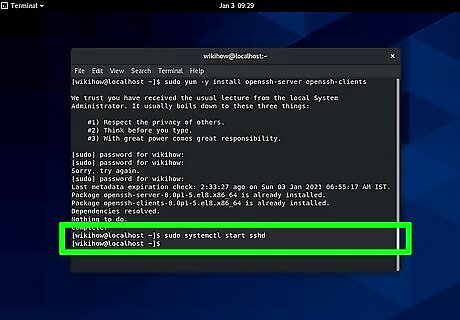
Enter the following code: sudo systemctl start sshd. With this active, the SSH service will start and will listen continuously for actions from clients, like connection requests.
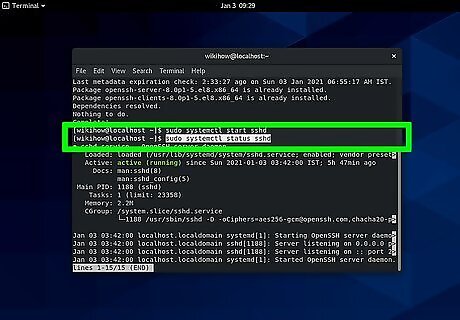
Enter the following code: sudo systemctl status sshd . You should see an "active" status. If you don't, you may need to restart your system and try again. To stop SSH, enter systemctl stop sshd and you'll see an "inactive" tag. If you want SSH to automatically start whenever you reboot the system, enter: sudo systemctl enable sshd. Change "enable" to "disable" if you want to cancel the automatic setting.


















Comments
0 comment