views
- Build muscle with a consistent exercise schedule featuring resistance training at least twice a week and cardio three times a week.
- Increase your caloric intake by opting for quality nutrients and healthy fats, and consume 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight per day to meet your daily caloric intake.
- Try strength training workouts such as squats, planks, pullups, deadlifts, and dumbbell presses to improve your muscle mass.
Creating an Exercise Routine to Build Muscle
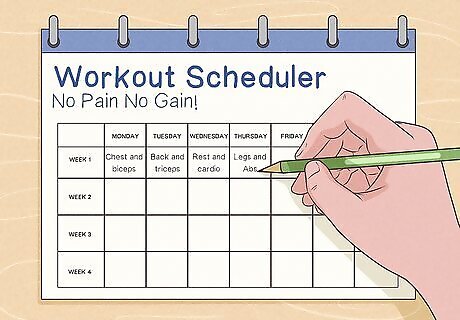
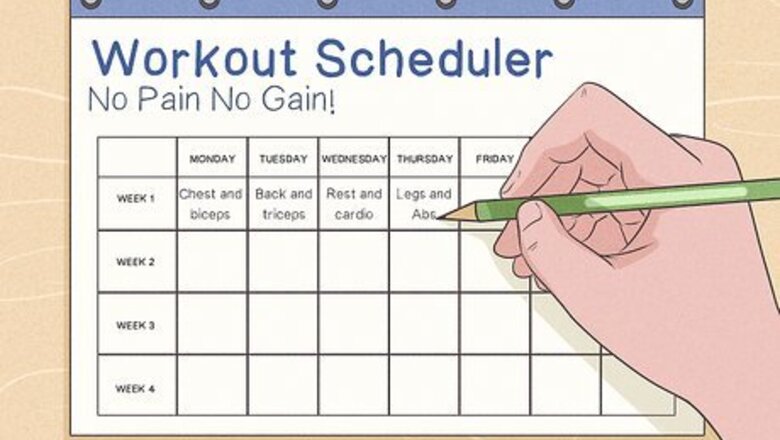
Create a consistent exercise schedule with resistance training and cardio. Resistance training helps build muscle, while cardio warms up the muscles and increases endurance. Dedicate 3 days a week for cardio and at least 2 days for strength training, including free weights or bodyweight exercises like squats, planks, or deadlifts. Perform each exercise for 3 sets of 6-12 reps to build 1 to 2 pounds (0.45 to 0.91 kg) of lean muscle per month. Example split routine: Day 1: Chest and biceps, starting with or followed by cardio Day 2: Back and triceps Day 3: Active rest day, cardio Day 4: Legs and abs Day 5: Shoulders, starting with or followed by cardio Day 6: Rest Day 7: Rest Example upper/lower split routine: Day 1: Upper-body workout, starting with or followed by cardio Day 2: Lower-body workout Day 3: Rest and cardio Day 4: Upper-body workout Day 5: Lower-body workout Day 6: Rest and cardio Day 7: Rest
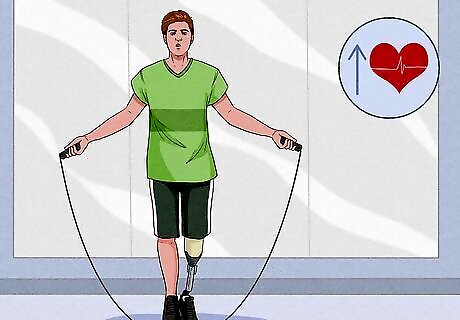
Warm up with 5-10 minutes of cardio exercise before lifting. Before you begin any exercise routine, start with a low-intensity routine designed to warm up all the muscles you're about to work on. This can include jogging, cycling, or the stair master. Not only will it help you get into the right frame of mind, but it can also help prevent injuries. The standard recommendation is 150 minutes of moderate cardio each week, 75 minutes of vigorous cardio, or an equivalent combination. Only warm up with stretches if you've already done at least 5 minutes of cardio to avoid injury. Cardio burns calories quickly, so overdoing it can limit your energy to build muscles. If you increase the amount of cardio exercise you do, be sure to increase your calorie intake as well.
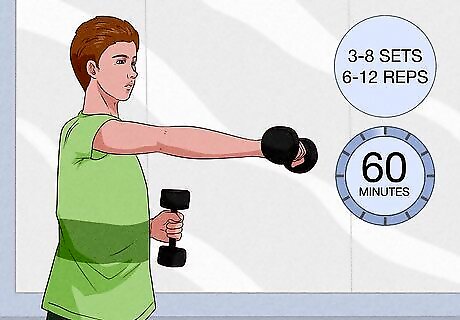
Work harder for a shorter length of time to build muscle. Training with high reps is good for building endurance but it won’t increase your muscle size or strength. Opt for shorter reps with heavier weights to build muscle. Aim for 3-6 sets per muscle group with 6-12 reps per set. Your final rep should be tough to complete! If not, increase the weight you’re lifting until you feel some resistance. Cap your workout time to 60 minutes a day. You'll be too tired to perform any more quality sets any longer.Tip: Every 4-8 weeks, vary your routine. As your body adapts to stress, you'll hit a plateau where the benefits of weight training will begin to diminish. The only way to prevent this is to switch things up. Increase your weights and change exercises.
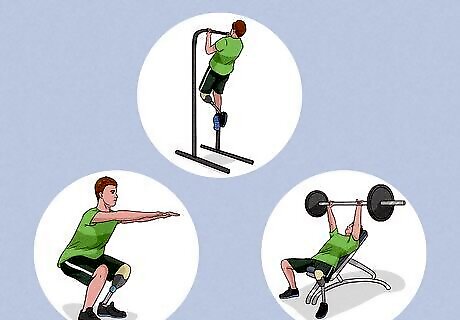
Work your whole body over the week. The more muscles you use when training, the more strength you'll gain and the more balanced your muscle development will be. Work your whole body simultaneously or target different muscle groups on different days. Give all your muscle groups equal attention. If you’re doing five sets of bench presses, follow up with five sets of rows. Doing so will encourage balanced training, growth, and flexibility. Compound exercises such as squats, deadlifts, presses, rows, and pull-ups use a lot of different muscles. They're great for a full-body workout. Don't rush. Advanced lifters base their routines around explosive repetition, where they lift heavy weights over a short (explosive) time. This method has significant benefits, but the risk of injury in novice athletes is high. It is recommended solely for more advanced athletes.
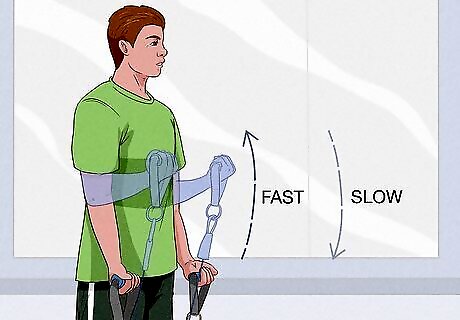
Practice explosive lifts to build strength. Explosive movement in exercise helps individuals increase their energy spending during and after resistance training, which helps with weight loss and muscle building. Start with a smaller range of motion to work up to the explosive part of your exercise (the lifting), but avoid full extensions at the peak of motion. For leg exercises, keep your knees slightly bent. For arm upper body exercises, keep your elbows slightly bent. Move slowly on the eccentric (lowering phase) as this part of the motion is a common cause of injury. Load the muscle at the low point of the exercise. This means holding the muscle contraction before beginning the movement. If you want to add explosive movements to your squats or other range-of-motion exercises, practice with a lighter weight and a low-intensity setup first.
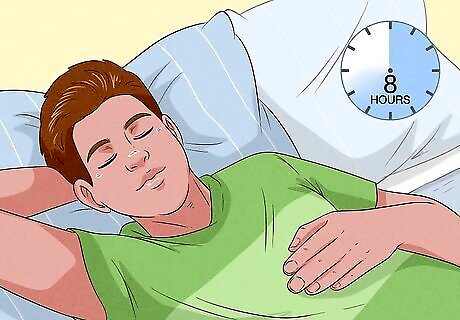
Get 6-8 hours of rest per day. Quality rest allows your body to repair and build your muscles. It helps to avoid over-training, as this can lead to muscle wasting, which is when you lose the ability to pump your muscles. Symptoms of over-training include: Chronic fatigue Strength loss Loss of appetite Insomnia Depression Lowered sex drive Chronic soreness Prone to injury

Reduce stress with slow movement, hobbies, or self-care. Whether stress comes from your job or home, or that's just how you're wired, do what you can to reduce or eliminate it. Stress also increases the hormone cortisol, which encourages your body to store fat and burn muscle tissue. Here are some examples of activities that reduce stress: Take a walk. Talk to a friend. Journal. Color in an adult coloring book. Play with your pet. Soak in a bathtub. Smell essential oils.

Invest in a personal trainer. If you're unsure how to start your muscle-building journey, invest in a personal trainer. Personal trainers know how to curate a tailored muscle-building workout that meets your goals. They can also provide alternative exercises if you have a specific health condition or injury. Similarly, working alongside a personal trainer will help maintain proper form and maximize each workout for effective results.
Muscle-Building Workouts

Perform pull-ups to work your back muscles. Grip a horizontal bar that is comfortably taller than you with your hands shoulder-width apart. Lift your legs back to hang from the bar. Pull yourself up, lifting your chin to the bar using only your arms. Then, lower yourself down to your starting position and repeat for 3 sets of 10 pullups. You can use either an overhanded or underhanded grip. This exercise will work your lats, traps, and rhomboids.

Do bent over rows to build your back. Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, about 6-10 inches (15-25 cm) behind a barbell or 2 dumbbells. Bend slightly at your knees, but keep your shins vertical. Bend forward at the waist with your spine and head straight. Lift the weight with an overhand grip to your lower chest or upper abdomen. Lower slowly until your arms are nearly extended, without touching the ground. Perform 3 sets of 10 reps.

Improve chest and pec muscles with bench presses. Start with weights you can lift comfortably. Then, lay back on a weight bench. If you are a beginner, try lifting the bar with 5 to 10 pounds (2.3 to 4.5 kg) on each side. Position your arms at shoulder-width apart, then grab onto the bar. Slowly lower the bar until it's at nipple level, then push up until your arms are fully extended upwards. Do 3 sets of 8-10 repetitions. If you can, add additional weight to each set. Once you have a few months of practice, slowly increase the weight and go down to 6-8 reps per set. Try to reach muscle failure at the end of the third set.Variation: For an added challenge, lift weights on an incline bench press. The incline is like the bench press, but one end of the bench is tilted about 40 degrees. Lifting the bar on an incline will be harder, so start with less weight than on the flat bench press.

Do push-ups for upper body strength. Get into a plank position with your arms positioned shoulder-width apart. Then, lower yourself down slowly until your chin reaches the floor. Slowly push yourself up to a starting position. Do 3 sets of 10 push-ups. The closer your hands are to one another, the more you'll work your triceps.
Perform deadlifts to work your thighs, glutes, and calves. Place a heavy barbell or 2 dumbbells on the ground in front of you. Keeping your back straight and your core engaged, slowly bend at your knees. Grasp the weight, then rise from the ground, keeping the weight close to your body. Then, slowly lower the weight back down to the floor. Do 3 sets of 10 reps. Keep all of your muscles engaged as you do your deadlifts. Use your lower body to help you lift the weights. EXPERT TIP Laila Ajani Laila Ajani Fitness Trainer Laila Ajani is a Fitness Trainer and founder of Push Personal Fitness, a personal training organization based in the San Francisco Bay Area. With over 10 years as a trainer and exercise specialist, Laila has expertise in competitive athletics (gymnastics, powerlifting, and tennis), personal training, distance running, and Olympic lifting. Laila is certified by the National Strength & Conditioning Association (NSCA), USA Powerlifting (USAPL), and she is a Corrective Exercise Specialist (CES). Laila Ajani Laila Ajani Fitness Trainer Try micro loading to help you gain muscle faster. If you're using barbells, you can load any weight you want on the side, so you can move your weight up by a pound, half a pound, or two pounds. If you can lift sets of 6 at 50 pounds and it feels heavy, try 52 pounds the following week. This will help you see progress quickly.

Target your glutes, thighs, hips, and calves with squats. Add weights to a barbell, then put it on a rack so it's lower than shoulder height. Duck under the bar and stand up so that the bar rests comfortably just below your neck. Keep your knees slightly bent and your legs slightly wider than shoulder width. Lift the bar off the rack and move backward 1 step so the weight rests on your back. Then, slowly lower yourself down into a squat. Exhale deeply and use your legs and hips to lift out of the squat. Do 3 sets of 8 squats. The weight should be heavy enough that squatting is difficult but possible. This may mean using a bar without weight if you're a beginner. A 90-degree bend at the knees is the safest option. Make sure your knee doesn't go past your toes.Variation: Do front squats with a weighted bar for an extra challenge. Rack a weighted bar just below shoulder level. Come up to the bar from the front, positioning the bar on the front shoulders. Cross your arms over onto the bar and walk it out. Keeping your back straight, bend your legs into a squat with your hips under the bar. Slowly rise back to a starting position.
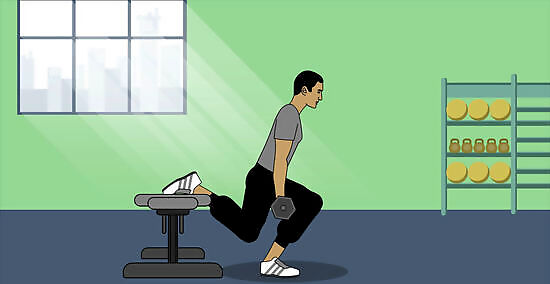
Work your legs with a Bulgarian squat. Hold a dumbbell in each hand, resting them at your sides. In front of a bench, lift your right leg back so it's parallel to the floor and rest comfortably on the bench. Bend into a squat using your left leg so the right knee almost hits the floor. Slowly rise back to your starting position. Repeat on the other side. Do 3 sets of 8 reps. Bulgarian squats are also called single-leg squats.

Do bicep curls to work out your arms. Sit down on a bench and pick up a dumbbell in one hand. With your elbow resting on your thigh, lift the dumbbell to your upper chest by curling your arm upward. Switch to the opposite hand and repeat. Do 3 sets of 8 reps.Variation: Do bicep curls with a weighted barbell to work both arms simultaneously. Stand up and grab hold of a weighted bar with both hands. Let your arms extend all the way down to your thighs. Using only your arms, lift the weight to your chest by curling your arms upward.

Target your triceps with dips. Place your hands shoulder-width apart on a bench, with your body and feet stretched out in front of you. Slowly bend your elbows and lower your body down so your butt nearly touches the floor. Use your arms to lift yourself back to starting position. Do 3 sets of 8 reps. If this isn't a high-intensity set for you, increase the resistance by lifting 1 foot off the floor. Dips are the most effective way to work your triceps, the muscle beneath your biceps. You'll need to have strong triceps to bench-press large amounts of weight.

Strengthen your arms with skull crushers. Lay down flat on a bench with a bar resting on the rack. Lift the bar over you, then bend your elbows so that the bar is close to your forehead. Slowly push the bar up until your arms are fully extended. Then, bring the weight back down. Keep your elbows close together as you lift and lower the bar. Repeat for 3 sets of 8 reps.

Build your shoulders with seated overhead presses. Sit on an incline bench so you’re sitting upright. Hold a barbell or dumbbells at shoulder height with your palms facing forward. Lift the weight above your head, keeping your elbows slightly bent to avoid hyperextension. Then, slowly lower the weights back to starting position. Do 3 sets of 8 reps.Variation: You can switch up this exercise by changing your hand and palm position. If you're using dumbbells, you can lift them until they touch overhead or lift them into a wide "Y" shape with your arms.

Perform crunches to work your core. Lie down on a mat and position both arms behind your head without locking your hands. Bend your knees so that your feet are flat on the ground. Push the small of your back into the ground and slowly roll your shoulders off the ground slightly. Then, slowly return to the floor. Repeat for 3 sets of 20 reps. Keep your movements slow and steady.Variation: For oblique crunches, angle your torso so 1 shoulder reaches toward the opposite knee. Alternate sides after each crunch.
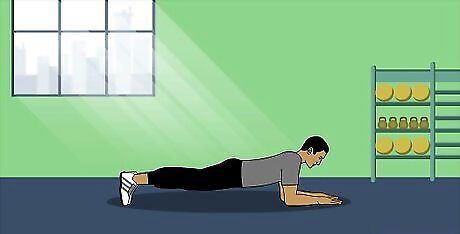
Work your abs with planks. Lie face-down on the floor. Place your hands under your shoulders. Then, lift yourself so you’re forearms are flat and your body is parallel to the floor. Keep your torso and legs stiff as you hold your position for as long as possible. Avoid arching your lower back or hiking your hips upwards. Try to hold your plank for 2 minutes. If you can't, rest for 1-2 minutes, then do a plank again. Do as many planks as it takes to reach 2 minutes. If you want to make the plank more intense, you can support yourself on your hands instead.
Muscle-Building Diet

Increase your calorie consumption by 10%. To gain weight, consume high-fat and high-calorie foods or beverages to bump your calorie count. Keep a log of the calories you eat each day and add those numbers together. Then, divide that number by the days of the week (7) to find your daily caloric needs. For example, if you ate 15,350 calories over the course of a week divide that by 7 to get an average of 2,193 calories per day. Make sure your calories are coming from a variety of healthy, minimally processed foods to provide quality nutrients for muscle-building.
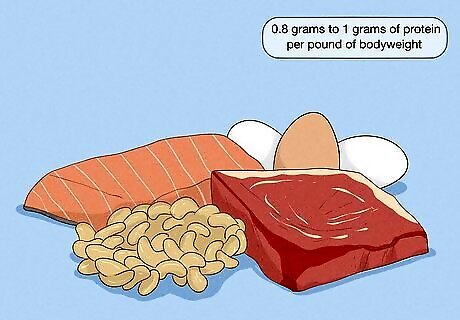
Eat 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight for muscle growth. Aim for about 0.8 to 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight (1.6g to 2g per kg). For example, if you weigh 180 lb, take 144-180 g of protein daily. If you're overweight, use your lean body mass as your body weight instead of your current weight. To determine your lean body mass, subtract your body fat percentage from your weight. You can use online body fat calculators to find out your body’s fat percentage which may require your body weight and measurements. You could meet a 120-gram daily protein goal by consuming high-protein foods like a 4-ounce broiled sirloin steak (33g), 2 cups of cooked lentils (36g), 4-ounce sockeye salmon (30g), and 4-ounce ham steak (22g). If you're having difficulty meeting these protein levels, you can always use protein shakes to make up the difference.
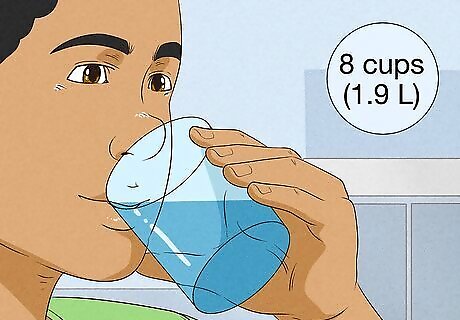
Drink at least 8 cups (1.9 L) of water each day. The body needs sufficient water to build muscle at an optimal rate. Aim to drink at least 8 cups (1.9 L), but you'll likely need more to build healthy muscle. Here's a great little formula to help make sure you are getting enough: Imperial units: Bodyweight in lbs X 0.6 = water intake in ounces. Metric units: Bodyweight in kg x 40 = water intake in milliliters. This includes all water from food and drink, not just glasses of water. If you are over 30, you can lower these numbers to lbs x 0.46 to 0.54 or kg x 30 to 35.
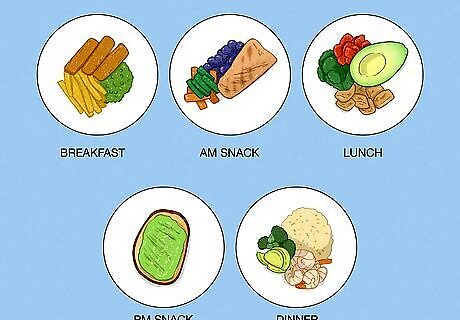
Eat small meals before and after exercising. To gain muscle, increase your calorie intake so your body has an energy surplus to support muscle growth. Instead of having 2-3 large meals, eat 5-7 smaller meals throughout the day. It helps if you're able to eat before and after your workout session, so you have the energy to expend and recover. To help keep your protein intake high, make 1 of your meals a protein shake. To make a basic shake, blend 8 ounces (230 g) skimmed milk, 1 banana, 1 tablespoon (15 ml) peanut butter, and 2 scoops of protein powder.
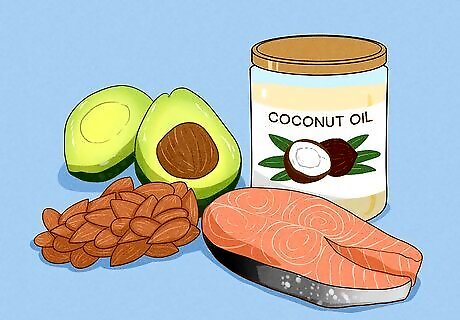
Consume healthy fats. Not only does it make food taste good, but fat is also good for you, as long as you eat the right amounts of fat! Saturated fats—the fat in a stick of butter, a bag of chips, or bacon—should be limited to about 20g or less. However, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are necessary to distribute vitamins A, D, E, and K and improve muscle-building and recovery times. Determine your fat intake by multiplying your calorie intake by 0.008 for maximum saturated fats and 0.03 for the "good fats." For example, for a 2,500-calorie diet, you would limit saturated fats to 20g or less and up to 75g of mono- and polyunsaturated fats. Monounsaturated fats can be found in olive, canola, sesame oils, avocado, and nuts such as almonds, cashews, peanuts, and pistachios. Polyunsaturated fats are found in corn, cottonseed, and safflower oils; sunflower seeds and oils; flaxseed and flaxseed oil; soybeans and soybean oil. Omega-3 fats are an ideal choice as they benefit the heart, blood, eyes, and, for children, brain development. It can be found in salmon, tuna, trout, sardines, and omega-3-enriched foods.

Take a multivitamin, as recommended by your doctor. In addition to a well-balanced diet, include a multivitamin supplement. It will ensure your body gets the full vitamins and minerals needed to stay healthy. There are many options, depending on your age, sex, and particular health and diet needs. Find the right one for you, and make it part of your daily routine. Alternatively, you can take a glutamine supplemental, to produce more glutamine, which is lost after an intense workout. Glutamine is a building block of protein which helps your body function and protect against injuries and compromised immune systems. Always check with your doctor before taking any vitamins or supplements.


















Comments
0 comment