views
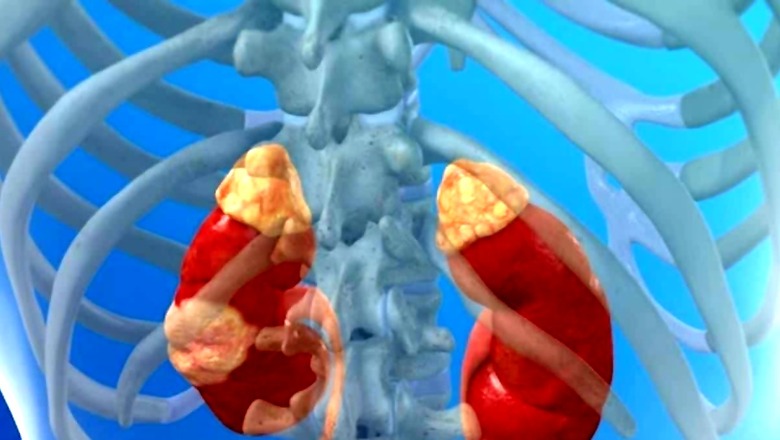
Kidney cancer is a condition that begins in the kidneys. It occurs when healthy cells in one or both kidneys grow uncontrollably and form a mass (known as a tumour). Most people experience no indications or symptoms in the early stages. Kidney cancer is typically found by coincidence during an abdominal (belly) imaging test for another problem. The reason kidney cells alter and become malignant is unknown. As per the National Kidney Foundation, as people get older, their chances of developing kidney cancer increase. There are several risk factors associated with kidney cancer. Renal cell carcinoma is the most frequent form of kidney cancer in adults. Other, less common kinds of kidney cancer can develop. Wilms tumour, a kind of kidney cancer, is more common in young children.
Kidney Cancer: Early Symptoms
Kidney cancer may not cause any symptoms in its early stages. When the tumour progresses, symptoms may arise. As a result, kidney cancer is frequently identified only after it has spread.
Signs and symptoms that may appear over time include:
– Blood in urine, which may seem pink, crimson, or cola-coloured
– Persistent pain in the back or side
– Loss of appetite
– Unexplained weight loss
– Tiredness
– Fever
Kidney Cancer: Risk Factors
The factors that can raise the risk of kidney cancer are:
1. Smoking: Nonsmokers are less likely to develop kidney cancer than smokers. After quitting, risk decreases.
2. Obesity: Obese people are more likely to develop kidney cancer than those who are regarded to be of healthy weight.
3. Old Age: Risk of developing kidney cancer rises with age.
4. Hypertension (high blood pressure): High blood pressure puts you at risk for kidney cancer.
5. People who undergo long-term dialysis to treat chronic renal failure are more likely to acquire kidney cancer.
6. A family history of kidney cancer increases the risk of developing the disease.
Kidney Cancer: Prevention
Taking actions to enhance your health may lower your risk of developing kidney cancer. To lower your risk, try:
– Quit smoking:
If you smoke, you should quit. There are numerous choices for quitting, including support groups, drugs, and nicotine replacement therapy. Tell your doctor you want to quit and talk about your choices.
– Control high blood pressure:
At your next appointment, ask your doctor to check your blood pressure. If your blood pressure is high, you can talk about options for lowering it. Exercise, weight loss, and dietary modifications can all be beneficial. Some people may require additional drugs to manage their blood pressure.
– Maintain healthy weight:
Work to keep a healthy weight. If you are overweight or obese, attempt to eat fewer calories each day and be physically active most days of the week. Ask your doctor about additional healthy weight-loss strategies.



















Comments
0 comment