
views
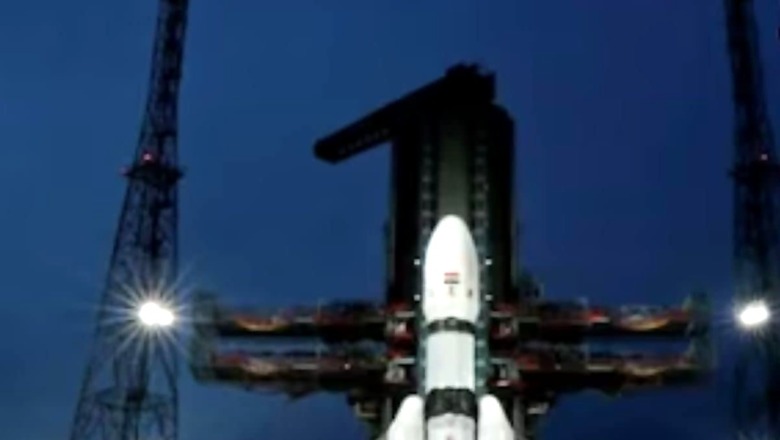
Chandrayaan-3, India’s third lunar mission, performed another significant manoeuvre on Monday and achieved a near-circular orbit around the moon. As per the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Chandrayaan-3 made the significant move between 11:30 am to 12:30 pm today.
“Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft undergoes another maneuver, achieves near-circular orbit around moon,” the ISRO posted on microblogging site X (formerly Twitter).
As the mission progresses, a series of maneuvers are being conducted by ISRO to gradually reduce Chandrayaan-3’s orbit and position it over the lunar poles.
This is the 2nd last orbit reduction maneuvers to bring the spacecraft closer to the Moon, after which the landing module, comprising the lander and rover will break away from the propulsion module. The next maneuvers is on August 16.
The lander is expected to undergo a “deboost” (the process of slowing down) and make a soft landing on the south-polar region of the Moon on August 23.
India’s ambitious third Moon mission’s spacecraft Chandrayaan-3 after the launch on July 14, had entered into lunar orbit or the Moon’s orbit on August 5.
Over five moves in the three weeks since the July 14 launch, ISRO had lifted the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft into orbits farther and farther away from the Earth.
Chandrayaan-3
Chandrayaan-3 is a follow-on mission to Chandrayaan-2 to demonstrate end-to-end capability in safe landing and roving on the lunar surface. It consists of lander and rover configuration.
It comprises an indigenous propulsion module, lander module, and a rover with an objective of developing and demonstrating new technologies required for inter-planetary missions.
The propulsion module will carry the lander and rover configuration till 100 km lunar orbit. The propulsion module has Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE) payload to study the spectral and polarimetric measurements of earth from the lunar orbit.
The mission objectives of Chandrayaan-3 are to demonstrate safe and soft landing on the lunar surface, to demonstrate rover roving on the Moon, and to conduct in-situ scientific experiments.
The lander will have the capability to soft land at a specified lunar site and deploy the rover that will carry out in-situ chemical analysis of the Moon’s surface during the course of its mobility.
The lander and the rover have scientific payloads to carry out experiments on the lunar surface.
(With PTI Inputs)
















Comments
0 comment