
views
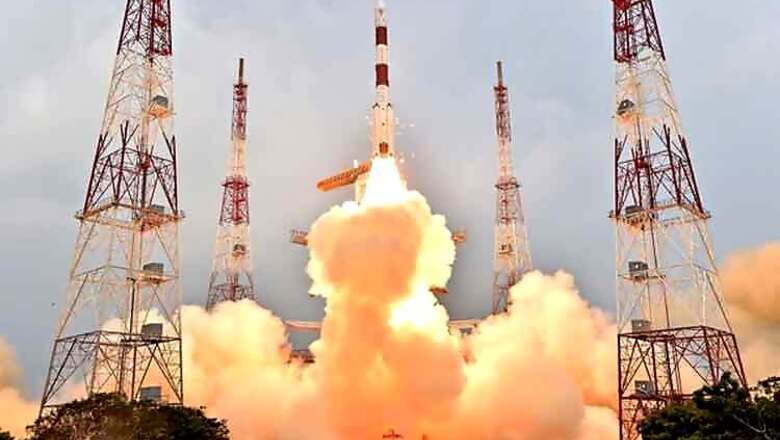
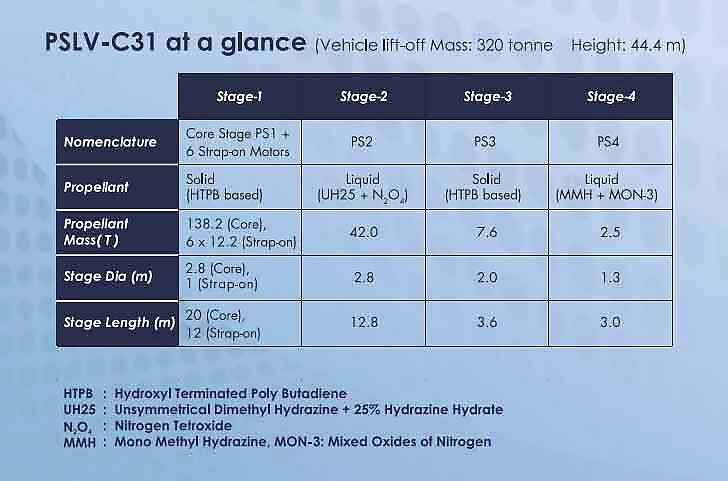
The Indian GPS is a very close to becoming a reality with the launch of the fifth regional navigation satellite system IRNSS-1E by the Indian Space Research Organisation on Wednesday. The Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle lifted off from the second launchpad of Satish Dhawan Space Centre at Sriharikota in Andhra Pradesh to put the IRNSS-1E, the fifth navigation satellite of the seven satellites constituting the IRNSS space segment, into its orbit.
IRNSS is an independent regional navigation satellite system being developed by India. It is designed to provide accurate position information service to users in India as well as the region extending up to 1500 km from its boundary, which is the primary service area of IRNSS.

IRNSS will provide two types of services -- Standard Positioning Service (SPS), which is provided to all the users and Restricted Service (RS), which is an encrypted service provided only to the authorised users. The IRNSS is expected to provide a position accuracy of better than 20 m in the primary service area.
IRNSS comprises of a space segment and a ground segment. The IRNSS space segment consists of seven satellites, with three satellites in geostationary orbit and four satellites in inclined geosynchronous orbit.
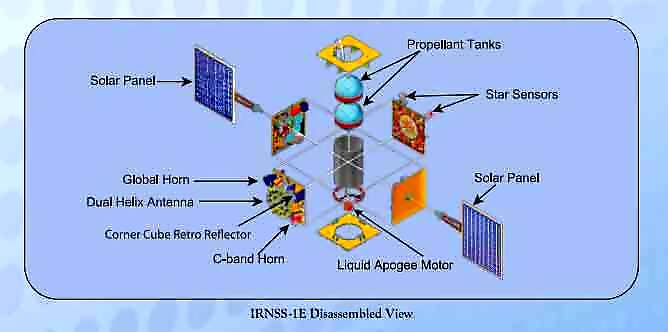
IRNSS ground segment is responsible for navigation parameter generation and transmission, satellite control, ranging and integrity monitoring as well as timekeeping.
The satellite has a lift-off mass of 1,425 kgs and its configuration is similar to that of IRNSS-1A, 1B, 1C and 1D.
The two solar arrays of the satellite consisting of Ultra Triple Junction solar cells can generate about 1,660 watts of electrical. Special thermal schemes have been designed and implemented for the some of the critical elements such as atomic clocks.
After injection into this preliminary orbit, the two solar panels of IRNSS-1E are automatically deployed in quick succession and the Master Control Facility (MCF) at Hassan takes control of the satellite and performs the initial orbit raising manoeuvres consisting of one manoeuvre at perigee (nearest point to earth) and three at apogee (farthest point to earth). For these manoeuvres, the Liquid Apogee Motor (LAM) of the satellite is used, thereby finally placing - it in the geosynchronous orbit at 111.75 deg E location with an initial - inclination of 28.1 deg with respect to the equator.

IRNSS -1E carries two types of payloads — navigation payload and ranging payload. The navigation payload will transmit navigation service signals to the users. A highly accurate Rubidium atomic clock is part of the navigation payload of the satellite. The ranging payload of IRNSS-1E consists of a C-band transponder which facilitates accurate determination of the range of the satellite. IRNSS-1E also carries Corner Cube Retro Reflectors for laser ranging.

Pictures courtesy: ISRO website


















Comments
0 comment