
views
Scientists make constant efforts to discover the secrets of the history of the universe. As per reports, the universe has not been this bright since its inception, and it experienced the ‘Dark Ages’ when thick gases would cloud rays of light emanating from the stars. So, today let’s take a look at how our space transformed from a dark space to a glowing set of millions of galaxies. Researchers used the Webb telescope to find the answer.
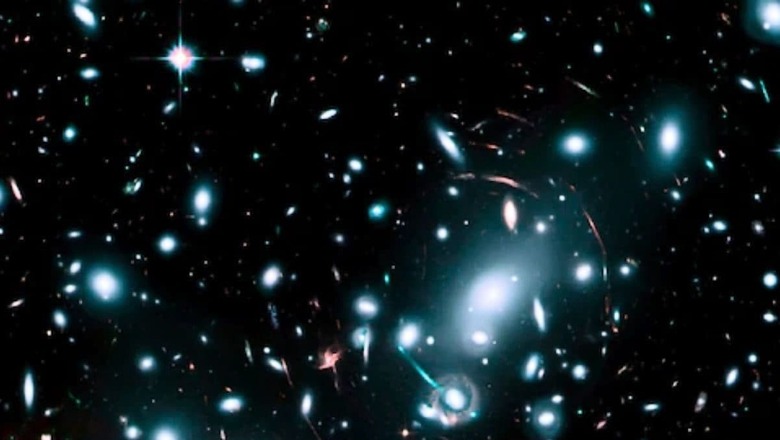
A photo of the “faintest galaxies” went viral a few weeks ago. The photograph was captured by the James Webb Space Telescope which features the smaller galaxies that first started emitting light. The post was shared on X on the page ESA. “The NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope has just observed some of the faintest galaxies in the universe! These dwarf galaxies existed in the earliest era of the universe, a time where there was darkness without any stars or galaxies, filled with a dense fog of hydrogen gas, just a few billion years after the Big Bang,” the tweeter reads.
The NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope has just observed some of the faintest galaxies in the Universe!These dwarf galaxies existed in the earliest era of the Universe, a time where there was darkness without any stars or galaxies, filled with a dense fog of hydrogen… pic.twitter.com/fVY92LiZgi
— ESA (@esa) February 28, 2024
To understand the phenomenon in depth, researchers pointed the telescope towards a region of the cosmos called Pandora’s Cluster. It is said to be a group of galaxies that are so massive that they warp space. This produces a curved cosmic lens that enlarges the objects outside of it. According to the American space agency NASA, “Light follows that bend instead of travelling in a straight line, distorting and brightening what’s behind the object.”
However, using that natural cosmic lens and the power of the telescope, scientists were able to discover some of the faintest and oldest galaxies in space. Reports suggest that the scientists observed small galaxies in a form that would have taken shape billions of years ago, due to the time it takes for light to reach us. The small galaxies generate massive amounts of ultraviolet light that are enough to disintegrate the massive gas clouds that have saturated space.
In the later stages of our universe, the starlight was no longer clouded by cosmic gases, and it began to glow as the star became clearer and brighter. Further, in this study published, scientists found that low-mass galaxies used to produce energetic radiation, and their combined effect was so great that it could change the entire state of the universe. In this way, the universe kept coming out of darkness and getting illuminated.



















Comments
0 comment