
views
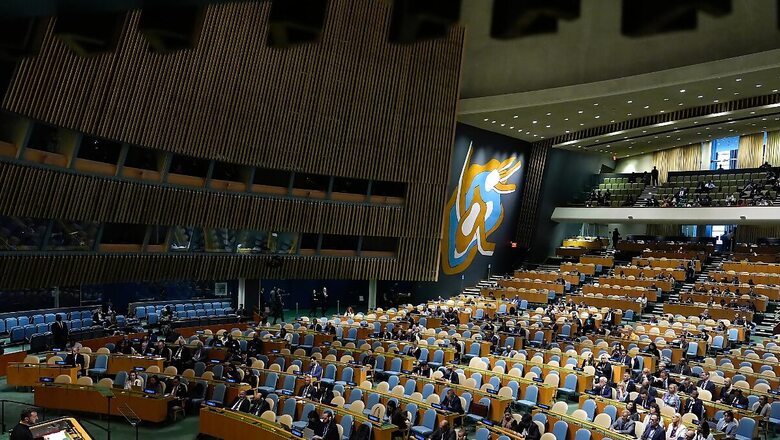
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) adopted an ambitious agreement last week which aims to make the organization more relevant and effective on the global stage in the 21st century. This agreement has been made to prevent wars and hold those who violate its Charter accountable. It is true that the United Nations has failed to prevent wars and conflicts in the last few decades. Seven countries, including Russia and Iran, opposed the Pact for the Future.
What is this agreement?
This treaty is a 42-page document, which states that the countries of the world should stand united and the 56 goals of the treaty should be implemented rapidly. It talks about working together to deal with challenges like climate change, Artificial Intelligence, conflicts, inequality and poverty so that the lives of eight billion people inhabiting the world can be improved. Seven members of the 193-member General Assembly opposed it.
Some of its proposals are quite promising, such as the request to the Secretary-General to review the status of the UN peacekeeping operations and the promise to work towards nuclear disarmament. However, as always, these are being seen as tall rhetoric.
Does this agreement explain how it will contribute to improving the world?
The agreement is full of big goals and commitments for the future but it lacks real, realistic steps on which the countries of the world are unlikely to move forward and implement them.
The document claims that nations will “end hunger and eliminate food insecurity”, commit to a fair multilateral trading system, achieve gender equality, protect the environment and climate, and protect people affected by humanitarian emergencies. However this pact is silent on how the UN and its members implement this.
Why did Russia oppose it? How many countries supported it?
Russian representative Sergei Vershinin proposed an amendment to the treaty at the very beginning. He said, “Nobody is happy with this treaty.” But 54 African countries strongly opposed Russia’s amendment.
The Republic of Congo proposed on behalf of the African countries not to vote for the amendment. This was also supported by Mexico.
During voting, this proposal of the African countries got the support of 143 countries, while only six countries- Iran, Belarus, North Korea, Nicaragua, Sudan and Syria, supported Russia. 15 countries abstained from voting.
Why has the United Nations talked about strengthening itself in the agreement?
The United Nations wants to have more powers in future so that its voice is heard and accepted, which will have an impact on the world. Therefore, the United Nations Security Council should be reformed. The treaty has expressed a commitment to make reforms in the 15-member Security Council of the United Nations so that it can better represent today’s world and remove the historical injustice against Africa. Africa has no permanent member in the Security Council. It also talks about correcting the lack of representation of the Asia-Pacific region and Latin America.
What are the other special aspects in this agreement, which were included in the Pact for the Future?
Leaders should give priority to dialogue and negotiation, end the ongoing wars in the Middle East, Ukraine and Sudan, bring rapid reforms in the international financial system, speed up the process of abandoning fossil fuels and listen to the younger generation by including them in the decision-making process.
What is the general response of member countries to this treaty?
The G77, the leading group of developing countries of the United Nations, which now has 134 members, supported the words of UN Secretary-General Guterres. Ugandan Prime Minister Robinah Nabanza said in the General Assembly that this treaty should not become just a formality but it should have political will and commitment at all levels of global leadership.
What are the challenges to this Pact? What can be expected?
The ‘Pact for the Future’ has come at a time when the world is going through huge changes. It warns that increasing destructive steps can push the world into a state of crisis and disintegration. This pact has sub-treaties like Global Digital Compact and Declaration on Future Generations.
Through this pact, for the first time in more than a decade, there have been talks of eliminating nuclear weapons. It also speaks about stopping the arms race in space and commitment to control the use of lethal automatic weapons. The Global Digital Compact talks about making the first global agreement on Artificial Intelligence (AI). There has been debate for some time about making laws on AI.
Why did it propose to strengthen the International Court of Justice so that its verdicts are obeyed?
As people are losing their lives in Israel’s war in Gaza and South Lebanon, the Russia-Ukraine war and the civil war in Sudan, the United Nations has shown commitment to support the International Court of Justice (ICJ). However, Israel has made it clear that it will not listen to the United Nations and the International Court of Justice on this matter.
Why are 7 countries including Russia and Iran opposing this treaty?
Russia, along with six other countries, has opposed the “Pact for the Future” of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA).
Russia argues that the treaty favours Western interests and does not adequately represent the concerns of other countries. Russian Deputy Foreign Minister Sergei Vershinin claimed that the drafting process was dominated by Western countries, which sidelined the input of Russia and its allies.
Russia has proposed an amendment stating that many of the issues addressed in the treaty fall under domestic jurisdiction and so the United Nations should not interfere in these matters. This amendment was rejected.
Russia objected to 25 elements within the treaty, including those related to gender rights and disarmament. The Russian delegation has expressed dissatisfaction with the language related to universal access to sexual and reproductive health rights, and has seen it as an imposition on national sovereignty.
Should this be seen as a setback for Russia, as most countries in the world have supported the Pact?
It could be a setback for Russia. Russia misread the diplomatic landscape by proposing amendments at a time when other nations were ready to move forward with the agreement. This miscalculation led to public setbacks for Russia as it failed to secure widespread support for its position.


















Comments
0 comment