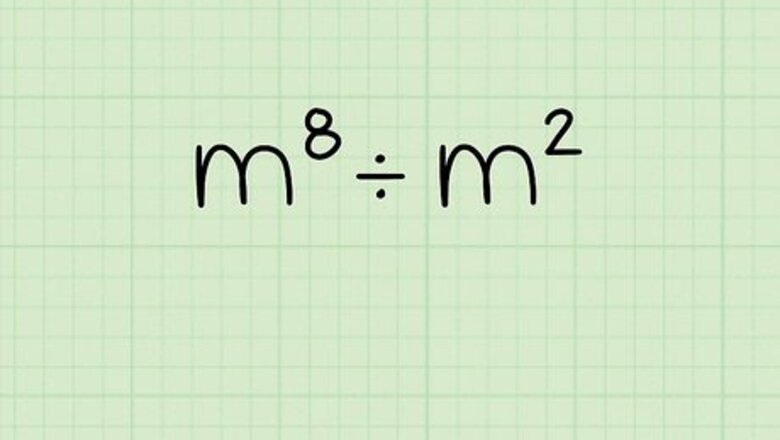
views
Understanding the Basics
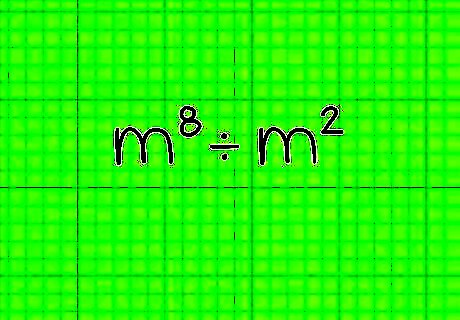
Write down the problem. The most simple version of this problem will be in the form of m ÷ m. In this case, you're working with the problem m ÷ m. Write it down.
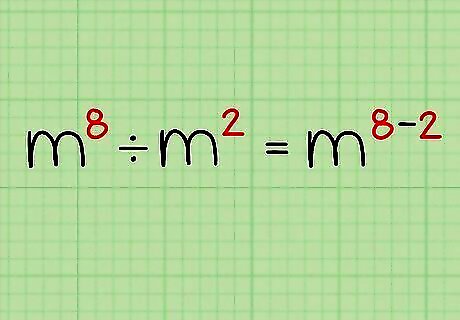
Subtract the second exponent from the first. The second exponent is 2 and the first is 8. So, you can rewrite the problem as m.
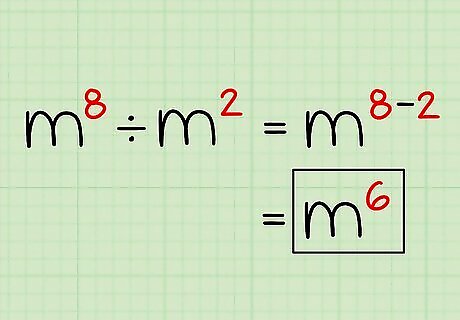
State your final answer. Since 8 - 2 = 6, your final answer is m. It's that simple. If you're not working with a variable and have an actual number in the base, such as 2, then you would have to do the math (2 = 64) to finish solving the problem.
Going the Extra Mile
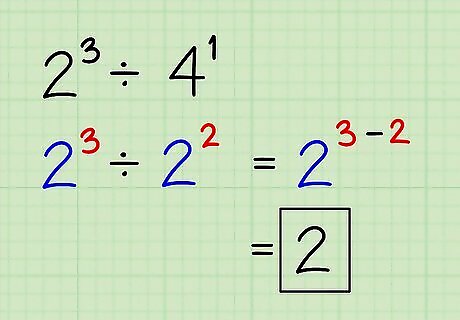
Make sure that each expression has the same base. If you're working with different bases, then you cannot divide the exponents. Here's what you need to know: If you're working with a problem with variables, such as m ÷ x, then there's nothing more you can do to simplify it. However, if the bases are numbers and not variables, you may be able to manipulate them so you end up with the same base. For example, in the problem, 2 ÷ 4, you first have to make both bases be "2." All you do is rewrite 4 as 2 and do the math: 2 ÷ 2 = 2, or 2. You can only do this, however, if you can turn the larger base into an expression of squared numbers to make it have the same base as the first.
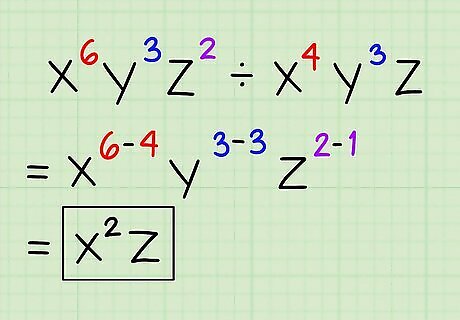
Divide expressions with multiple variables. If you have an expression with multiple variables, then you just have to divide the exponents from each identical base to get your final answer. Here's how you do it: xyz ÷ xyz = xyz = xz
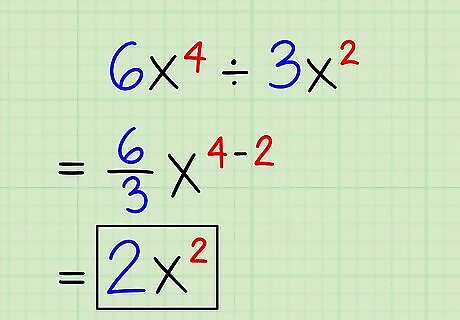
Divide expressions with coefficients. As long as you're working with the same base, it's no problem if each expression has a different coefficient. Just divide the exponents as you normally would and divide the first coefficient by the second. Here's how: 6x ÷ 3x = 6/3x = 2x
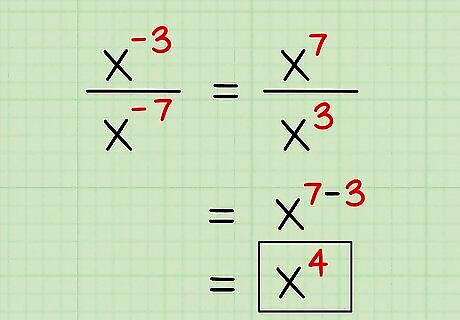
Divide expressions with negative exponents. To divide expressions with negative exponents, all you have to do is move the base to the other side of the fraction line. So, if you have 3 in the numerator of a fraction, you'll have to move it to the denominator. Here are two examples: Example 1: x/x = x/x = x = x Example 2: 3xy/xy = 3y/(x * xy) = 3y/xy = 3/x

















Comments
0 comment