
views
Confirming the Baby Bird’s Age and Level of Injury
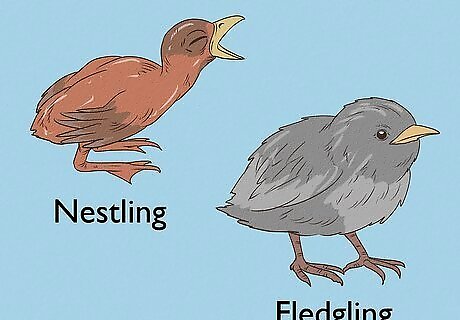
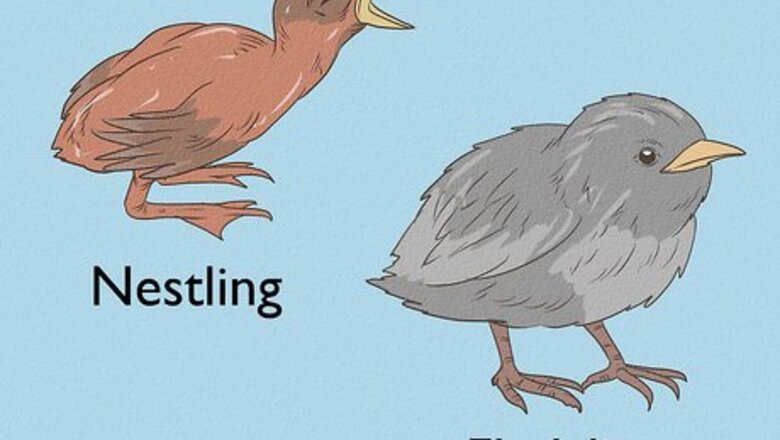
Determine if the bird is a nestling or a fledgling. To best help the baby bird, you will need to first determine how young the bird is and how far along it is in its development. A nestling has very few feathers and/or will be covered in fluffy down, their eyes will be closed, or they will just barely open. These are very young birds who should remain in the nest, as they are still highly dependent on their parents for nurturing and food. A fledgling is older than a nestling and they will usually have lots of feathers on their bodies. Fledglings are encouraged or even pushed out of the nest by their parents. They will usually spend two to five days on the ground once they are out of the nest, flapping their wings and hopping about. However, their parents will keep close watch on them from a distance and continue to feed and nurture the fledgling until they learn how to fly, eat, and protect themselves from predators.

Note if the baby bird’s parents and/or nest is nearby. Another way to determine if the baby bird is in danger is to check if there is a nest in a nearby tree or perch close to the baby bird. You may also notice adult birds perched close to the baby bird and observing the baby bird. If you see a nest or parents nearby, and the bird is a fledgling, you may be fine to leave the baby bird alone. If you see a nest close to a nestling, you can pick up the baby bird carefully and put it back in the nest. It is a myth that the smell of humans will cause the parents to reject the baby bird, as birds do not have a strong sense of smell. The baby bird should be nurtured and fed by the parents once you put it back in the nest. You may need to observe the fledgling for at least an hour to determine if the parents are nearby or to spot the baby bird interacting with it’s parents. Make sure the parents visit the baby bird in the nest to confirm the baby bird is not orphaned or alone.

Check if the bird is injured or appears ill. Look for signs of injury on the bird, like a broken limb, bleeding on the bird’s body, and missing patches of feathers (if the bird is a fledgling). The bird may also be shivering or making low noises. You may also notice a dead parent or parents nearby or in the nest, as well as the presence of a cat or a dog that may have injured the bird. If you see any signs of illness or injury, or if the parents are dead or do not return to the nest after two hours, you may need to make a temporary nest for the baby bird and then bring it to the nearest wildlife rehabilitation center.

Avoid interacting with a fledgling if it is not injured and it is close to its nest. If the bird is a fledgling and it does not appear ill or injured, you should leave it alone to continue its development on the ground. However, you should prevent any household pets, such as cats, from getting close to the bird and watch it to make sure it can hop away from an area with any hazards or predators. Do not try to feed the fledgling, as birds have specific and unique diets. As well, giving the bird water could be a drowning hazard. EXPERT TIP Roger J. Lederer, PhD Roger J. Lederer, PhD Ornithologist Dr. Roger Lederer is an Ornithologist and the founder of Ornithology.com, an informative website about wild birds. Dr. Lederer has spent over 40 years teaching, studying, and writing about birds. He has traveled to over 100 countries to study birds. Dr. Lederer is an Emeritus Professor of Biological Sciences at California State University, Chico, and has been a Department Chair of Biological Sciences and Dean of the College of Natural Sciences. He has written more than 30 research papers and 10 books on birds and a textbook entitled “Ecology and Field Biology.” Dr. Lederer has consulted the BBC, National Geographic, National Public Radio, ABC News, the Guinness Book of World Records, and numerous other organizations and publications. Roger J. Lederer, PhD Roger J. Lederer, PhD Ornithologist Don't assist fallen fledglings. Fledgling birds exploring the ground after leaving nests still depend on parental care. While tempting to intervene, young birds are developmentally ready to hop on the ground, strengthening wings until they fledge completely.
Making a Temporary Nest for the Baby Bird
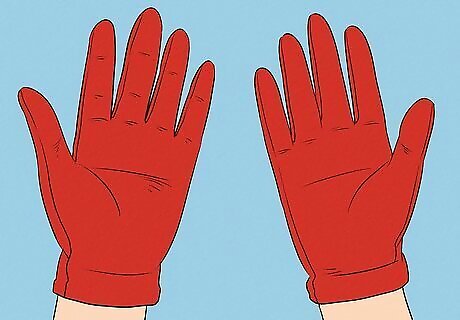
Wear gloves when handling the bird. Protect yourself from disease and parasites, as well as the sharp beaks and talons of the bird by using gloves. You should also wash your hands before and after handling the bird, even if you are wearing gloves.

Make a hanging nest if the bird’s parents are nearby but the nest is destroyed. If the bird’s nest is clearly destroyed but the bird’s parents are close by, you can create a simple hanging nest for the birds. Use a small basket or a small tupperware container. Punch or cut holes on the bottom of the container and line the container with paper towels. Hang the nest with duct tape to a branch near the old nest. Place the baby bird in the hanging nest. The parent should then locate the new nest and the baby bird.
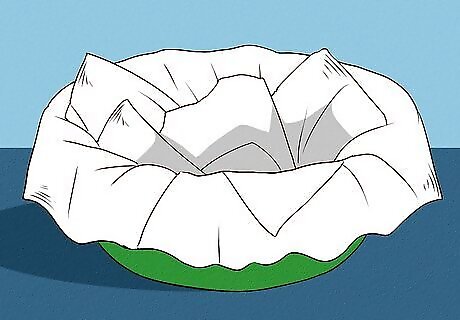
Create a nest from a small plastic bowl and paper towel if the bird is orphaned. It is important that you do not put the baby bird back in the original nest if it is injured and its parents are missing, as the nest may contain parasites that could weaken the bird further. Instead, build a temporary nest for the bird using a small plastic bowl or a berry box. You should line the bowl with unscented paper towel to provide some cushioning for the bird. Avoid using a wire cage as the wire can injure the bird’s delicate feathers. If you do not have access to a plastic bowl, you can use a paper bag with air holes.
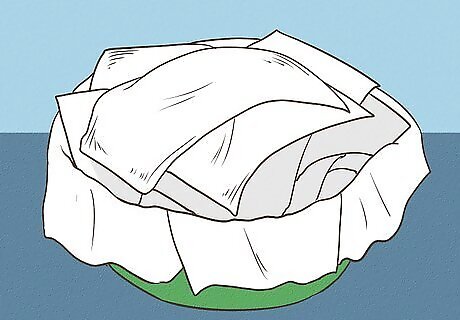
Place the bird in the nest and cover it with a paper towel. This will keep the bird warm and protect it when it is in the temporary nest. If the bird is shivering, you can warm it up by putting one end of the cardboard box on a heating pad set to low. You can also fill a hot water bottle and place it next to the bird in the bowl. Make sure the bottle does not touch the bird, as this could burn it, or leak, as this could chill the bird even further.
Put the nest in a warm, quiet, and dark area. Once you place the bird in the lined plastic bowl, you can put the bowl in a cardboard box and tape the box shut. Put the box in a spare room or a bathroom away from pets and children. Noise can be very stressful for the bird so make sure all radios and televisions are turned off. You should limit your contact with the baby bird so you do not make its injury or illness worse. Make sure the baby bird’s legs are tucked underneath its body, not stretched out.

Do not feed the baby bird. Every species of bird requires a specific diet, so avoid making the bird more ill or weak by giving it food it should not eat. When a bird is injured, it will use all its energy to fight shock and the injury so do not force it to devote its energy to eating as well. You should also avoid giving the bird water, as it can potentially drown the bird.
Wash your hands after handling the bird. If you touch the bird, you should wash your hands well to prevent the transfer of any diseases or parasites. You should also wash any items the bird was in contact with, like towels, blankets or jackets.
Seeking the Help of a Wildlife Rehabilitator
Contact your local wildlife center. Once you create a temporary nest for an injured or orphaned bird, you should reach out to your local wildlife center. You can locate the nearest wildlife center by contacting: Your state wildlife agency The Humane Society in your area A local veterinarian that specializes in wildlife or exotic animals The US Fish & Wildlife Service The Wildlife Rehab Info Directory

Describe the condition of the baby bird. Once you get in touch with a wildlife rehabilitation center, you should describe the bird’s symptoms and provide information on if the bird is a fledgling or a nestling. You should also note where you found the baby bird in the wild, as the wildlife center may use this information when releasing the bird.

Transport the baby bird to the care of the rehabilitator. Bring the baby bird, in its temporary nest, to the nearest rehabilitation center for treatment as soon as possible so it can be treated and released back into the wild. Though you may be tempted to keep the baby bird and treat it yourself or keep it as a pet, the baby bird is considered a wild animal. It is illegal to keep a wild animal in your home and keeping the bird can put the life of the bird in danger.

















Comments
0 comment