
views
The second wave of the pandemic has struck the nation hard with a daily surge in the total number of confirmed cases, creating fear and panic among citizens and forcing many states to impose various restrictions to control the spread of the pandemic and break the chain of transmission.
As of 22 April 2021, India recorded 3,15,735 new confirmed cases (22,84,411 active cases of COVID-19) with the most affected state being Maharashtra. Adding to the worry is the experts’ claim of the mutant strain of COVID-19 being more severe and infectious. While research is ongoing with experts and virologists analysing the new strain, it is important to understand the symptoms and risks to protect ourselves and prevent its spread. The age group of 60+ and those with co-morbidities are at higher risk of developing serious illness. However, anyone can contract COVID-19 and become seriously ill or succumb to the disease irrespective of age.
The most common symptoms of COVID-19 are fever, dry cough and fatigue. But other symptoms that some patients experience are shortness of breath, loss of taste or smell, chest pain, nasal congestion, conjunctivitis, sore throat, headache, muscle or joint pain, skin rash, nausea or vomiting, diarrhoea, chills or dizziness. People with such symptoms should get tested immediately and seek timely medical care. Unidentified asymptomatic cases i.e. infected individuals not showing any symptoms are a major concern as they may unknowingly spread the infection to others.
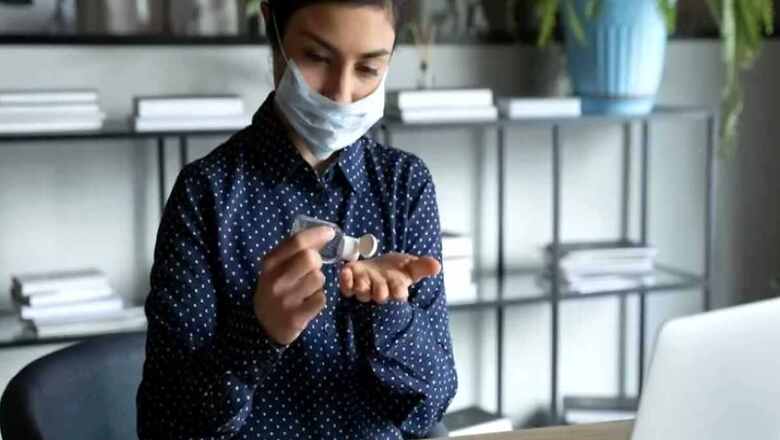
Government and healthcare experts have been consistently sending messages on COVID-appropriate behaviour like physical distancing, wearing a mask, keeping rooms well ventilated, avoiding crowds or close contact with others and maintaining good hygiene. Good hygiene includes sanitizing your hands with hand rub, hand wash or soap and water, avoiding touching eyes, nose and mouth, covering your mouth and nose with your bent elbow or tissue while coughing or sneezing and cleaning/disinfecting frequently touched surfaces. It is also important to get tested if you have any signs/symptoms of COVID-19 or you could have come in close contact with a known case of COVID-19
Currently, there the number of COVID testing facilities providing RT-PCR tests free of cost have increased at government centres, while private labs offer the test by collecting the sample from your home at a cost. Due to a rise in the number of tests performed daily, there is further delay in receiving confirmed reports proving detrimental. Therefore, anybody experiencing symptoms of COVID should self-isolate at home until the test result is received. Early testing, timely treatment, COVID-appropriate behaviour and vaccination will prevent mortality and rapid spread.
Anyone having signs or symptoms of COVID-19, can get the test done either at home or any of the COVID testing facilities. In case identified as positive, the person should first reach out to the COVID-19 helpline in their locality and the hospital directly as bed-allocations and admissions are done in coordination with the administration based on the availability of beds.
By: Dr. Mukesh Mohode & Dr. Shailesh Wagle – NGO Partner United Way Mumbai















Comments
0 comment