
views
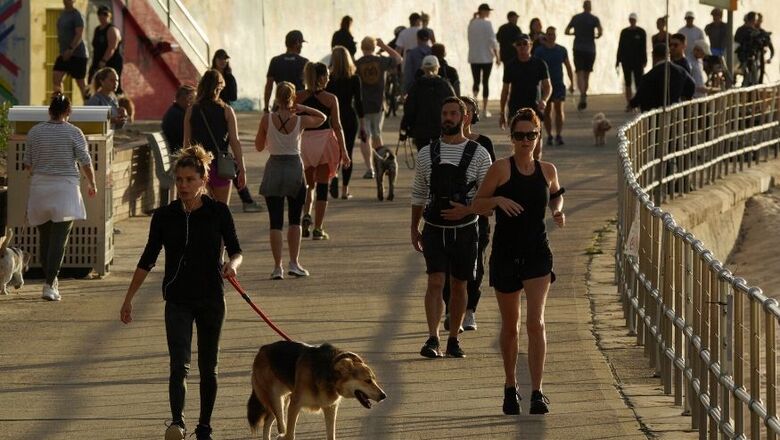
While higher heat and humidity may slow the spread of COVID-19, longer hours of sunlight are associated with a higher incidence of the disease, according to a study.
The research, published in the journal Geographical Analysis, indicates that sunny days can tempt more people out even if this means a higher risk of infection.
The findings by researchers led by McMaster University in Canada inform the widespread scientific debate over how seasonal changes, specifically warmer weather, might shape the spread of COVID-19.
While research has shown that pathogens such as influenza and SARS thrive in lower temperatures and humidity, little is known about SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, the researchers said.
There is a lot of pressure to reopen the economy, and many people want to know if it will be safer to do so in the summer months, they said.
"Restrictions in movement, which have begun to ease around the world, hinge in part on how SARS-CoV2 will be affected by a change in season," said Antonio Paez, a professor at McMaster, and lead author of the study.
Paez and colleagues investigated climate factors in the spread of COVID-19 in several provinces in Spain, one of the countries hardest hit by the pandemic, with more than 270,000 cases.
They combined and analysed data on reported cases of the disease and meteorological information over a period of 30 days that began immediately before a state-of-emergency was declared.
At higher levels of heat and humidity, researchers found that for every percentage increase, there was a 3 per cent decline in the incidence of COVID-19, possibly because warmer temperatures curtail the viability of the virus.
The opposite was true for hours of sunshine: more sun meant greater spread, they said.
The researchers speculate the increase may be related to human behaviour, since compliance with lockdown measures breaks down in sunnier days.

















Comments
0 comment