views
- Use .\filename.exe to run an EXE from the current directory in PowerShell.
- To run an EXE from another directory, you can use & "C:\Windows\notepad.exe"
- To use the Start-Process cmdlet to run the program, type Start-Process -FilePath "filename.exe"
Using .\ (Dot Slash)
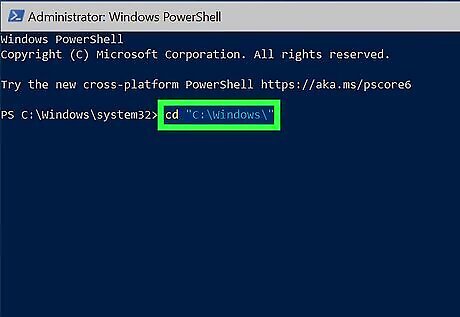
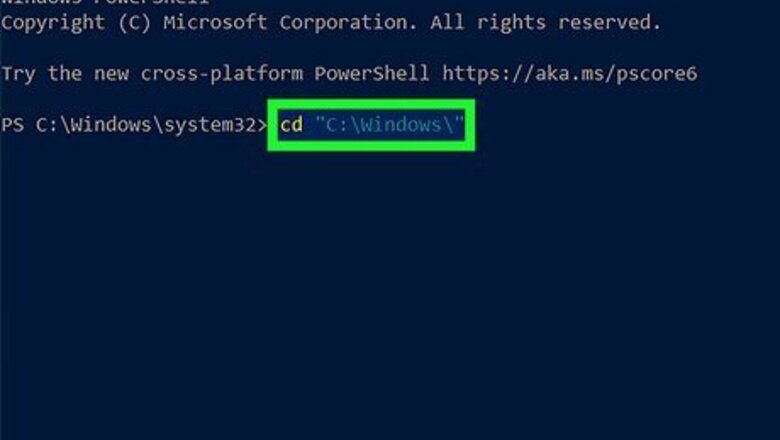
Use cd to enter the directory that contains the EXE file. For example, if you want to run notepad.exe from PowerShell, type cd "C:\Windows\" and press Enter.
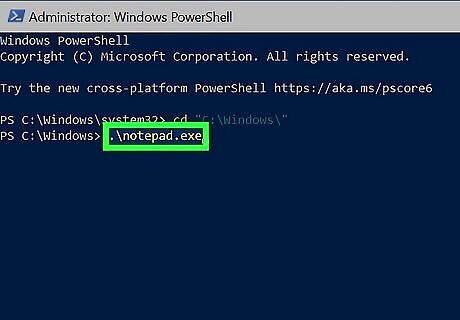
Enter the command to run the EXE file. To run an EXE file from the current directory in PowerShell, you'll need to preface the filename with .\. For example, to run notepad.exe, type .\notepad.exe and press Enter. Typing the .\ before the filename tells PowerShell you want to run the EXE file from the current directory. If you want to run the EXE file from a different directory, use the call operator (&).
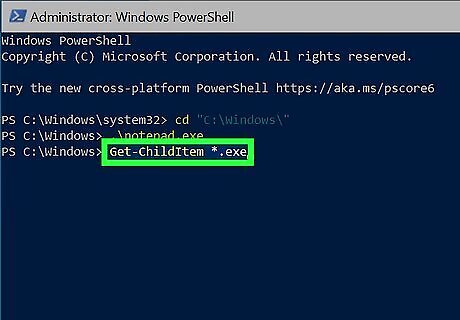
Use Get-ChildItem to locate EXE filenames (if needed). If you get an error that says, "The term (EXE file name) is not recognized as a name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or executable program," you're either entering the wrong file name or in the wrong directory. Get-ChildItem shows you all files and permissions in the current directory. To show only EXE files, use Get-ChildItem *.exe. You can also use Get-ChildItem to list files in other directories. For example, to show all executable files in C:\Program Files\Ableton\Live 11 Lite\Program, you'd use "C:\Program Files\Ableton\Live 11 Lite\Program\*.exe".
Using the Call (&) Operator
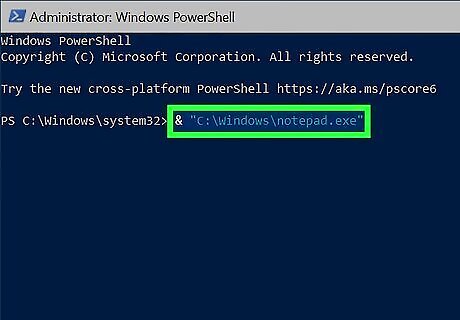
& "C:\Windows\notepad.exe". In PowerShell scripting, you can run any command that's stored in a variable by prefacing its path with an ampersand (&). Similarly, you can use the call operator to run an EXE file from the PowerShell prompt.
Using Start-Process Cmdlet
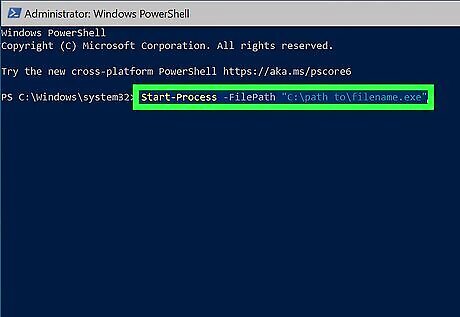
Start-Process -FilePath "filename.exe". This command will run the executable file called filename.exe from the current directory. If you're not already in the same directory as the EXE file, use the full path to the file, e.g., Start-Process -FilePath "C:\path to\filename.exe". If you need to run an EXE with parameters, enter the parameters after the executable's name. For example, to open Notepad with the window maximized, you'd use Start-Process -FilePath "C:\Windows\notepad.exe" -Wait -WindowStyle Maximized.
Using Invoke-Expression Cmdlet
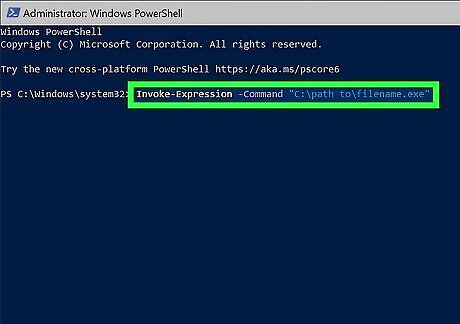
Invoke-Expression -Command "C:\path to\filename.exe". Invoke-Expression is typically used in PowerShell scripts to evaluate expressions, run scripts, and run commands in variables. You can also use it to run any EXE file at the prompt. Microsoft cautions against using Invoke-Expression in PowerShell scripts that accept user input unless the script can verify that the command is safe to run.


















Comments
0 comment